These guidelines on sustainability provide AusAID staff, contractors, NGOs and other implementing partners
with practical guidance on how to address sustainability issues more explicitly and effectively throughout the
activity management cycle.
What is sustainability?
Definition
In the context of donor-funded development programs and projects, sustainability can be defined as: the
continuation of benefits after major assistance from a donor has been completed.
Environmental sustainability has been defined as meeting the needs of the present
without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs. For the
purposes of the N.C. Environmental Stewardship Initiative, this definition is the guiding
philosophy.
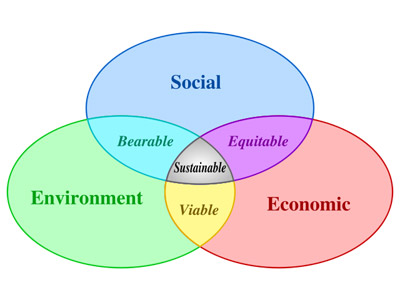
Organizations operate within an environmental, social and economic context.
Environmental sustainability is a part of this operation and best achieved when integrated
with other components.
An environmentally sustainable organization seeks to participate within its community
and seeks to balance economy, society and environment within its operations. Through seeking
balance, an organization may better steward natural and economic resources taking into account
the needs of future generations.
In daily practice, many opportunities exist to consider environmental sustainability. The
following demonstrates possible environmentally sustainable practices.
• Manufacturing can target the use of less toxic materials and use of recycled
feedstock over virgin feedstock, implement pollution prevention practices in
various processes, use reusable and recyclable transport packaging, and set
energy and water efficiency goals.
• Suppliers can be targeted for assistance in reducing packaging of raw materials
and in searching for less toxic supplies and processes, and provision of “greener”
energy supplies.
• Product Impact can be examined for opportunities to increase end of life
recycling or reuse, and to reduce overall environmental impact.
• Office operations can reduce paper usage through double-sided copying and
printing, use of e-mail, beginning or expanding recycling programs for office
discards, and buying recycled office supplies.
• Purchasing can seek to define and establish environmentally preferable
purchasing, procuring supplies that are nontoxic and made with recycled content,
specifying that purchased items be delivered in bulk or with minimal packaging,
and establishing environmental screening for all new purchases.
• Transportation can include reducing employee car miles through
teleconferencing and trip consolidation, encouraging the use of carpooling and
mass transit by employees, considering alternative-fueled vehicles for motor
pools, and maximizing routing of product and raw material supply to minimize
trip miles.
• Food Service can include encouraging energy and water efficiency in cooking
and water operations; providing washable, reusable dinnerware; implementing
recycling programs for cans, bottles and other discards; donating excess food to
area “food rescue” programs; and establishing composting programs for food
wastes that cannot be donated.
• Facility Management and Housekeeping can include installing water-saving
devices such as low-flow toilets and aerators on sink fixtures; maximizing energy
efficiency in lighting, heating and cooling; using the least toxic cleaning
materials; and employing green building techniques in maintenance and
renovation practices.
• Landscaping can include evaluating the use/application of fertilizers, pesticides
and herbicides; reducing or eliminating building and grounds landscape to
conserve water; monitor watering systems to use only when needed; and
establishing composting programs for organic wastes.
• Interactions with the public can include informing the public and customers
about sustainability efforts and encouraging them to participate.
It is expected that organizations that are recommended to become Environmental
Stewards show leadership in this area, implementing and demonstrating examples of
environmentally sustainable practices.
USEFUL PDF FILES:
1. Promoting Practical Sustainability
 3. Sustainability Definition
3. Sustainability Definition 


No comments:
Post a Comment